
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has produced the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe to date. Known as Webb’s First Deep Field, this image of galaxy cluster SMACS 0723 is overflowing with detail.Thousands of galaxies – including the faintest objects ever observed in the infrared – have appeared in Webb’s view for the first time. (Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, and STScI)
What is the universe expanding into if it’s already infinite? – Mael, age 10, Missoula, Montana
When you bake a loaf of bread or a batch of muffins, you put the dough into a pan. As the dough bakes in the oven, it expands into the baking pan. Any chocolate chips or blueberries in the muffin batter become farther away from each other as the muffin batter expands.
The expansion of the universe is, in some ways, similar. But this analogy gets one thing wrong – while the dough expands into the baking pan, the universe doesn’t have anything to expand into. It just expands into itself.
It can feel like a brain teaser, but the universe is considered everything within the universe. In the expanding universe, there is no pan. Just dough. Even if there were a pan, it would be part of the universe and therefore it would expand with the pan.
Even for me, a teaching professor in physics and astronomy who has studied the universe for years, these ideas are hard to grasp. You don’t experience anything like this in your daily life. It’s like asking what direction is farther north of the North Pole.
Another way to think about the universe’s expansion is by thinking about how other galaxies are moving away from our galaxy, the Milky Way. Scientists know the universe is expanding because they can track other galaxies as they move away from ours. They define expansion using the rate that other galaxies move away from us. This definition allows them to imagine expansion without needing something to expand into.
The expanding universe
The universe started with the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago. The Big Bang describes the origin of the universe as an extremely dense, hot singularity. This tiny point suddenly went through a rapid expansion called inflation, where every place in the universe expanded outward. But the name Big Bang is misleading. It wasn’t a giant explosion, as the name suggests, but a time where the universe expanded rapidly.
The universe then quickly condensed and cooled down, and it started making matter and light. Eventually, it evolved to what we know today as our universe.
The idea that our universe was not static and could be expanding or contracting was first published by the physicist Alexander Friedman in 1922. He confirmed mathematically that the universe is expanding.
While Friedman proved that the universe was expanding, at least in some spots, it was Edwin Hubble who looked deeper into the expansion rate. Many other scientists confirmed that other galaxies are moving away from the Milky Way, but in 1929, Hubble published his famous paper that confirmed the entire universe was expanding, and that the rate it’s expanding at is increasing.
This discovery continues to puzzle astrophysicists. What phenomenon allows the universe to overcome the force of gravity keeping it together while also expanding by pulling objects in the universe apart? And on top of all that, its expansion rate is speeding up over time.
Many scientists use a visual called the expansion funnel to describe how the universe’s expansion has sped up since the Big Bang. Imagine a deep funnel with a wide brim. The left side of the funnel – the narrow end – represents the beginning of the universe. As you move toward the right, you are moving forward in time. The cone widening represents the universe’s expansion.
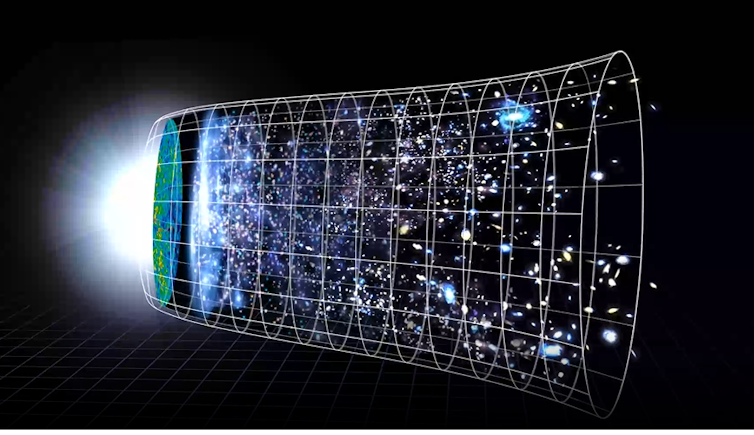
Scientists haven’t been able to directly measure where the energy causing this accelerating expansion comes from. They haven’t been able to detect it or measure it. Because they can’t see or directly measure this type of energy, they call it dark energy.
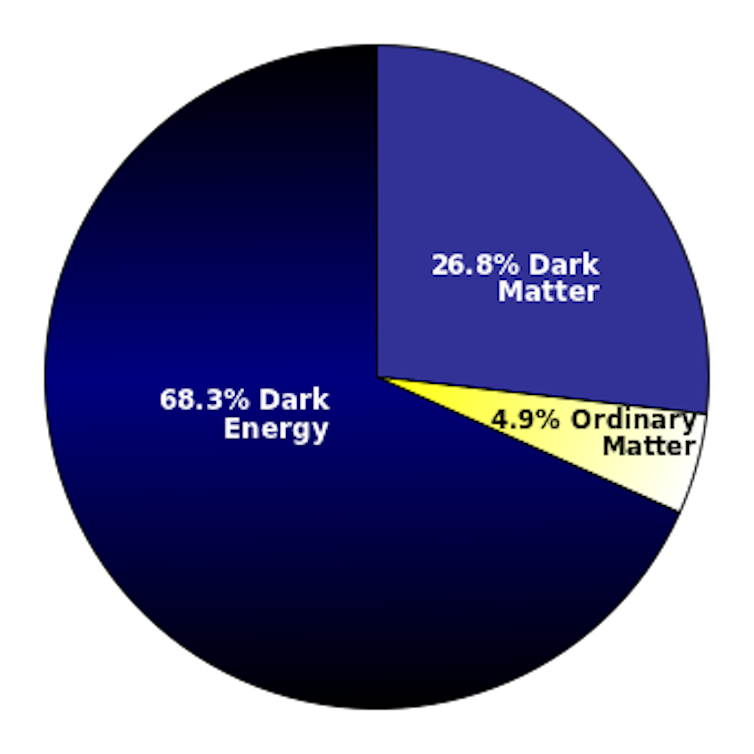
According to researchers’ models, dark energy must be the most common form of energy in the universe, making up about 68% of the total energy in the universe. The energy from everyday matter, which makes up the Earth, the Sun and everything we can see, accounts for only about 5% of all energy.
Outside the expansion funnel
So, what is outside the expansion funnel?
Scientists don’t have evidence of anything beyond our known universe. However, some predict that there could be multiple universes. A model that includes multiple universes could fix some of the problems scientists encounter with the current models of our universe.
One major problem with our current physics is that researchers can’t integrate quantum mechanics, which describes how physics works on a very small scale, and gravity, which governs large-scale physics.
The rules for how matter behaves at the small scale depend on probability and quantized, or fixed, amounts of energy. At this scale, objects can come into and pop out of existence. Matter can behave as a wave. The quantum world is very different from how we see the world.
At large scales, which physicists call classical mechanics, objects behave how we expect them to behave on a day-to-day basis. Objects are not quantized and can have continuous amounts of energy. Objects do not pop in and out of existence.
The quantum world behaves kind of like a light switch, where energy has only an on-off option. The world we see and interact with behaves like a dimmer switch, allowing for all levels of energy.
But researchers run into problems when they try to study gravity at the quantum level. At the small scale, physicists would have to assume gravity is quantized. But the research many of them have conducted doesn’t support that idea.

One way to make these theories work together is the multiverse theory. There are many theories that look beyond our current universe to explain how gravity and the quantum world work together. Some of the leading theories include string theory, brane cosmology, loop quantum theory and many others.
Regardless, the universe will continue to expand, with the distance between the Milky Way and most other galaxies getting longer over time.
Nicole Granucci is an instructor of Physics at Quinnipiac University.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.








The BIG question: what is space composed of that energy of all forms resides within?
I’ve always believed in the possibility of infinite universes where every possible outcome exists simultaneously. Or, as an alternative, successive universes which are built from the fabric of the previous one.